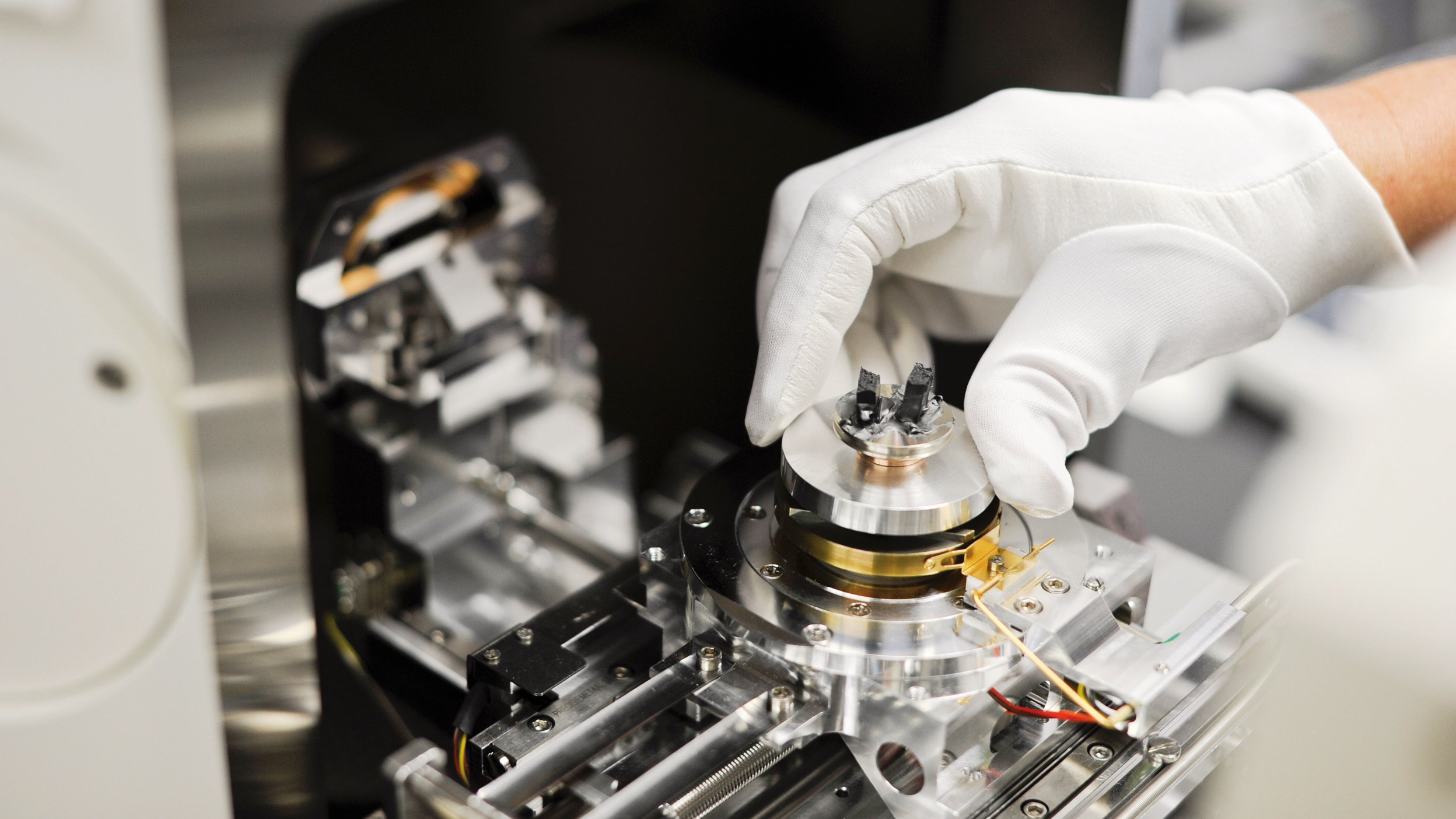
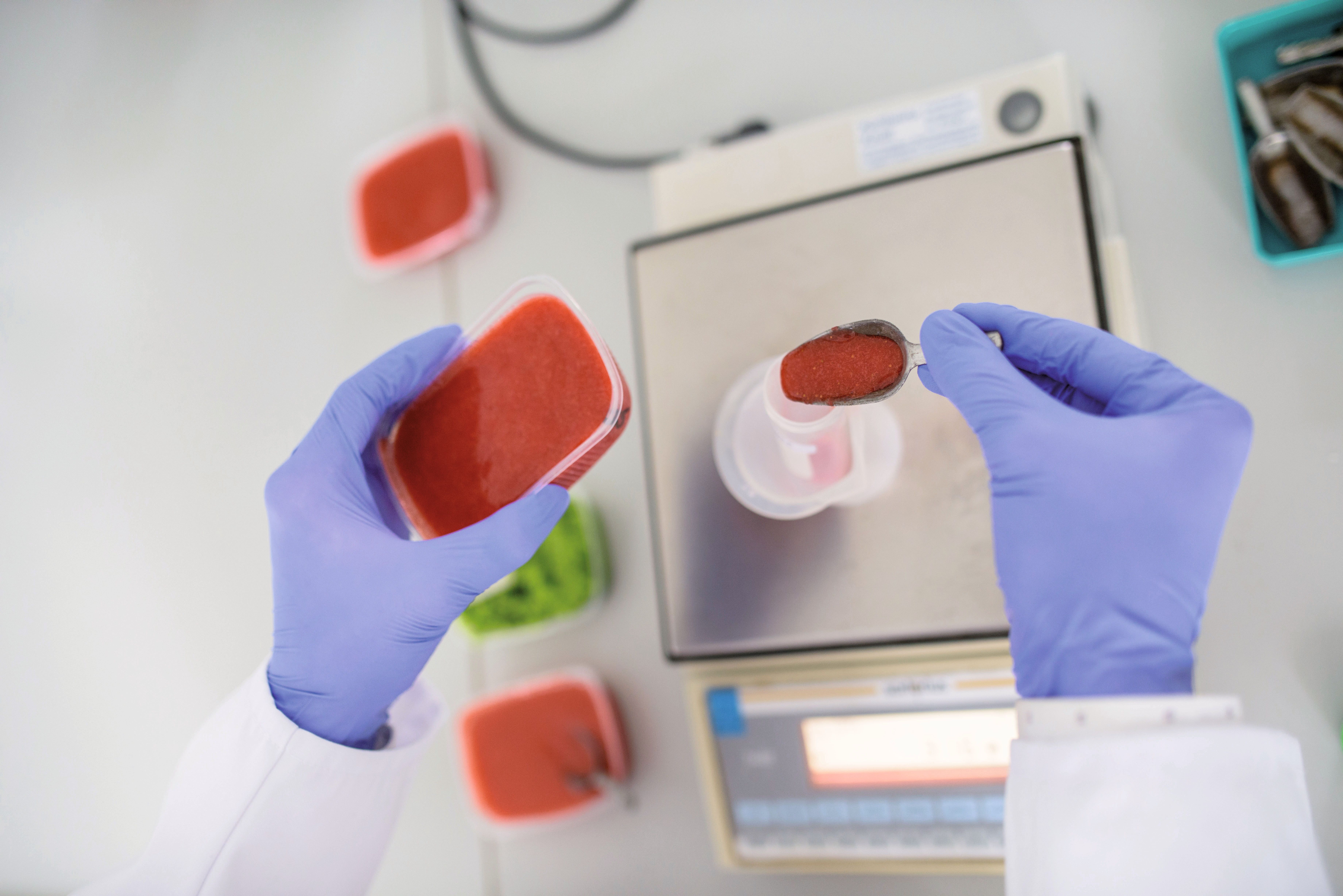
Engineers need a broad basic knowledge of science, technology and computer science for their work. In addition, sustainable technologies have become increasingly important due to the climate and energy transition, which is also reflected in the large selection of specialised degree programmes.
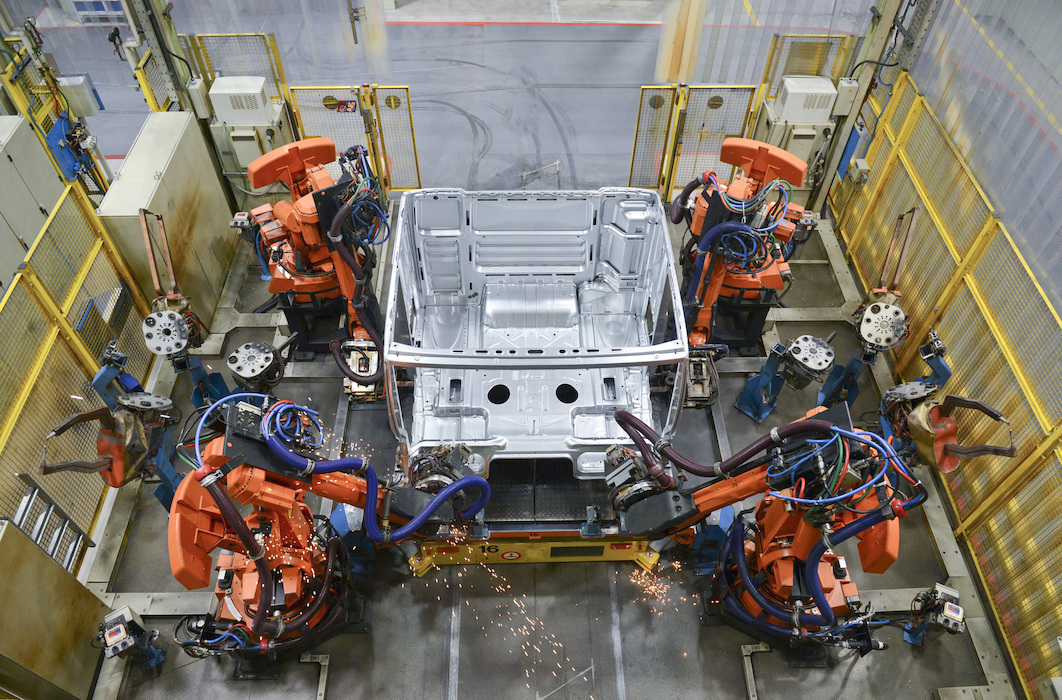
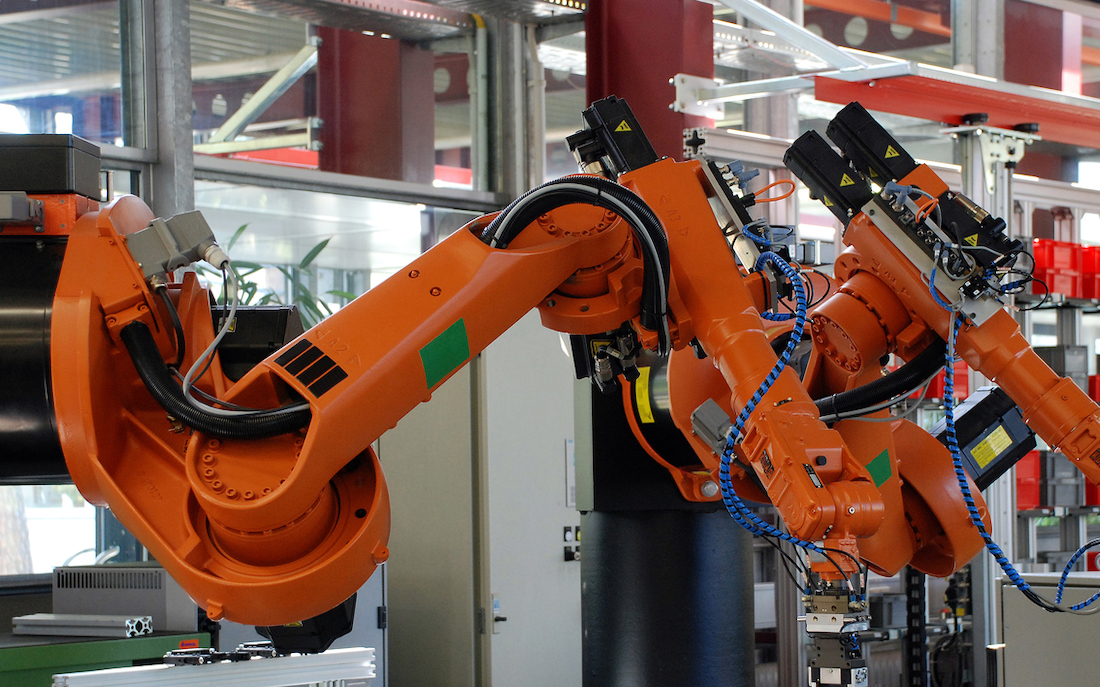
Engineering scientists are also at the forefront of the application of artificial intelligence in industry; automated production lines would be inconceivable without their broad knowledge of IT and technology. The subjects of maths, physics, chemistry, computer science, biology and technology are central to engineering studies. How much these areas are in focus of an engineering degree programme can vary greatly. For example, biology is almost non-existent in some degree programmes, while in others computer science and programming play at most a minor role. In most engineering degree programmes, students also acquire basic knowledge in the fields of economics, social sciences and law, business administration and project management in order to be prepared for management positions.
Due to global economic relations, foreign language skills and openness to other cultural areas also play a major role, especially with regard to the Asian markets. In addition, the teaching of overarching qualifications is part of an engineering degree programme, for example in the form of employee management, presentation techniques and rhetoric or marketing. This often takes the form of compulsory elective subjects.